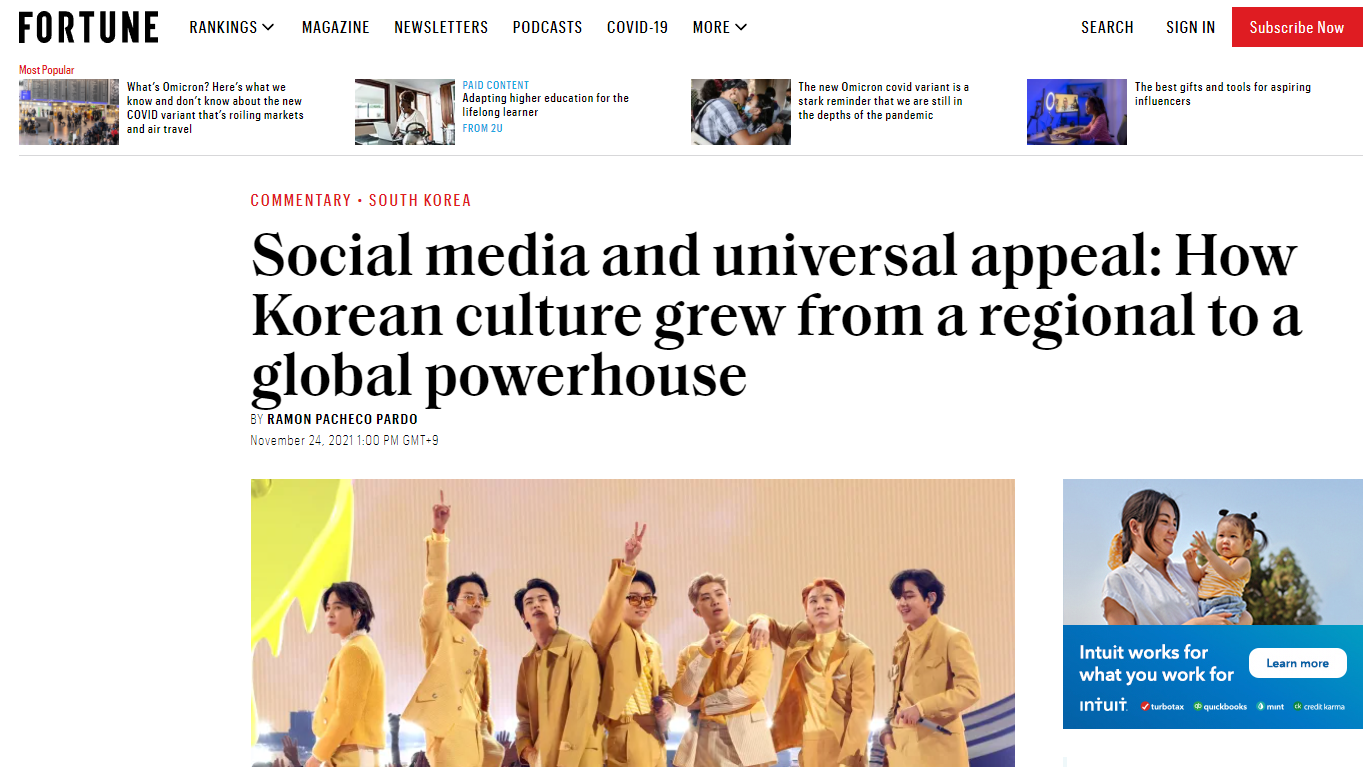
br1 Asia has already consumed Korean culture for more than 20 years.In the early brbr90s, the emergence of Seo Taiji and children became the beginning of K-pop, and in the late brbr90s, in the early 2000s, it hit China and Japan with BoA and Winter Sonata.In the mid-2000s, Latin America and the Middle East became influential.brbrbr2 The weakness of the Korean economy rather helped develop the Korean cultural industry.The size of the brbr small market has become an essential requirement to enter overseas markets, and the brbr Korean government has actively fostered the IT industry.The geopolitical characteristics surrounded by brbr powers served as a background for actively accepting foreign cultures.brbrbr3 In the 2000s, Korea and Japan competed for cultural leadership in Asia.Brbrvina Girls’ Generation came across the Pacific Ocean, but it didn’t resonate that much.Korean films such as brbr old, but bats, were awarded at the world’s leading film festival, but were completely shunned in the West.brbr4 In the 2010s, Korean agencies targeted the brbr fan base through social media such as YouTube Twitter rather than traditional media methods. In addition, it was easy to approach through !universal topics such as the gap between the rich and the poor!Brbrbr5 Some critics argue that Korean culture is! A national project! Dozens of countries are supporting the cultural industry, but it is not sweeping the world like brbr Korean culture. It was difficult to imagine the influence of Korean culture 10 years ago.brbr The global success factor of Korean culture was the early realization of the importance of social media and how to reflect social problems in culture.brbr That is the decisive answer that Korea has emerged as a world-class cultural powerhouse beyond Asia’s unrivaled cultural powerhouse.brbrbr. There are many articles analyzing Korean culture in American and British media these days.